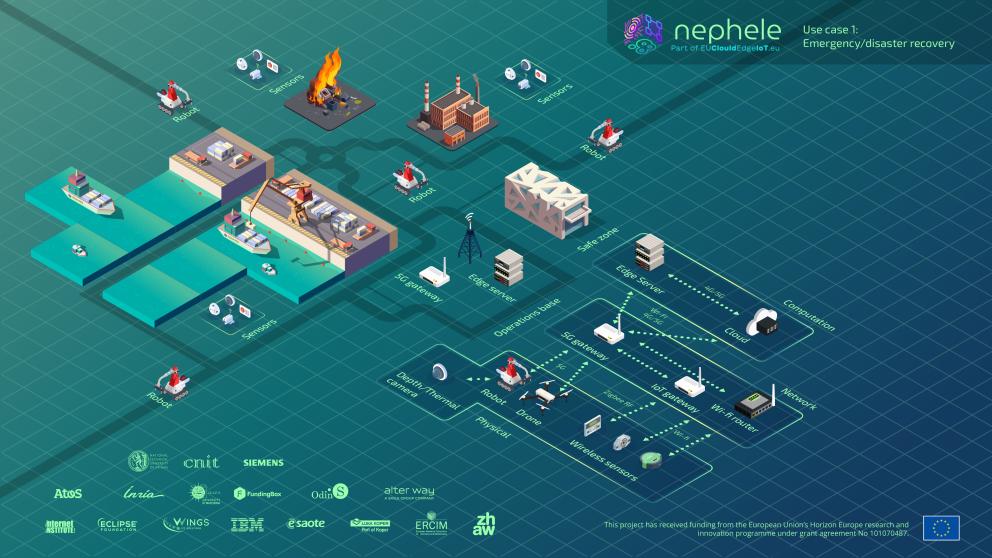
NEPHELE Use Case 1 - Emergency/Disaster Recovery aims to enhance the awareness for first responders (e.g., firefighters, emergency services) and collect data to prioritize rescue operations. The use case showcases the advantages of using the VOStack in complex robotic software implementations in emergency and disaster scenarios. More specifically, it shows a navigation mapping detection and assessment solution in an unknown environment.
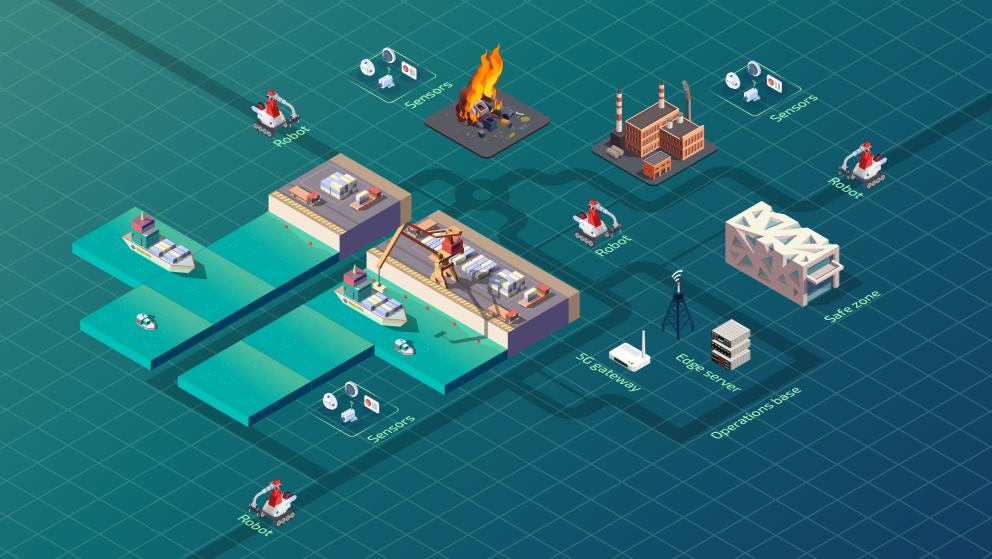
During the demo day at the Luca Koper Port, our robots were deployed to simulate an emergency scenario involving a fallen container with and unknown and potentially dangerous liquid, showcasing how autonomous systems can assist in such critical situations. A phone call was placed to alert the firefighting and security teams to respond to the fallen container emergency at the port. The security team quickly arrived to secure the area, clearing the way for our robotic team to step in and begin the missions.
The first mission involves drone-based mapping. The second mission focuses on mapping and detection using a ground robot. The third mission involves sensor deployment and the fouth and final task is liquid sampling. (Coordinates for sampling are obtained from the liquid detection and localization previous processes).
In this use case we evaluated several KPIs. These are some of our results:
- Victim detection and assessment: This KPI measures how accurately the system detects and classifies victims in tests. Both precision and recall were perfect, with no false positives or false negatives.
- Time to task completion: Our system outperformed all targets. Mapping, sensor deployment, liquid sampling, and victim detection were completed up to 20 times faster than expected, enabling swift and effective emergency response.
Scenarios
- Mapping: map a given area using ground robots and/or drones through cameras and lidars
- Victim detection and injury assessment: detect victims and assess their injuries in the post-disaster area using ground robots and/or drones
- Risk prediction: predict possible risks in a post-disaster area using ground robots, drones, and sensor nodes
- Device deployer and liquid sampler: physically deploy sensor nodes or take samples using ground robots
- Network and device monitoring: monitor the network connectivity for the IoT devices (robots, sensor nodes, drones) deployed in the post-disaster area
Goal
The goal of this use case is to enhance the situational awareness for first responders (e.g., firefighters) and collect data to prioritize rescue operations.
Description
Offer timely support to rescue teams by:
- Deploying network infrastructure for data collection and establishing contact with potential victims.
- Mapping the area and locating victims and risks.
- Providing dynamic monitoring to assess damages and victims’ injuries.
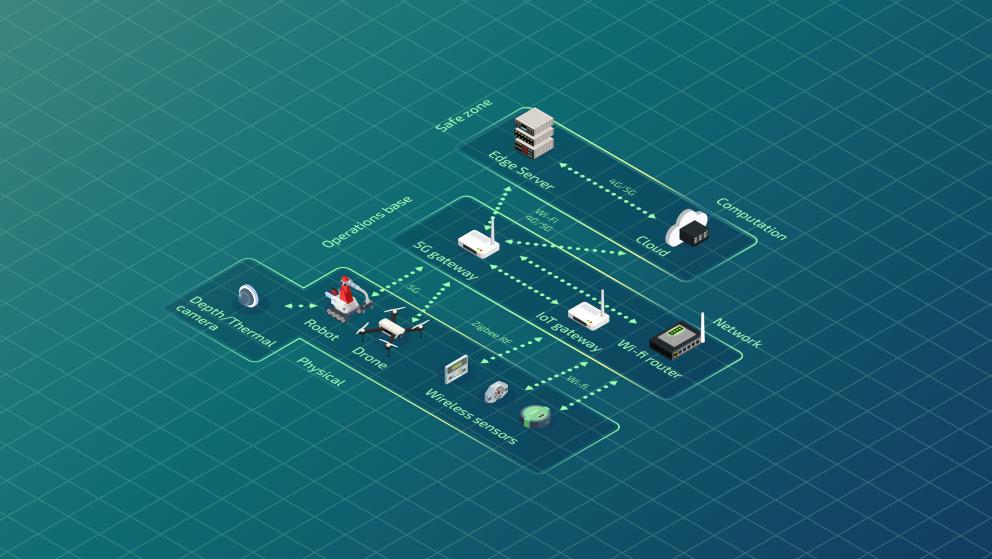
- Considering that data is generated from the heterogeneous IoT devices
2. Software components orchestration
- Dynamic placement of components based on service requirements and resource availability
- Performance and monitoring at the various levels of the continuum for dynamic components redeployment
3. Low latency communication
- Low delay communication networks to/from disaster area
- Support for mobility conditions and possible disconnections
4. Dynamic multi-robot mapping and fleet management
- Coordination, monitoring and optimization of the tasks allocation for mobile robots that work together (through their VO)
5. Computer vision for information extraction
- AI and computer vision for position detection from image and video data
6. Smart data filtering/aggregation/compression
- Large amount of data
- from sensors, robots and cameras in the intervention area
- Some can be filtered, others can be downsampled or aggregated before sending it to the edge/cloud
- Smart policies should be defined (high degree of data heterogeneity)
7. Robots and sensor nodes interaction
- Enable direct communication among robots and sensor nodes of the WSN by defining interaction guidelines
8. Monitoring Dashboard
- GUI to monitor the post-disaster operation from the operation base (data visualization and control command)