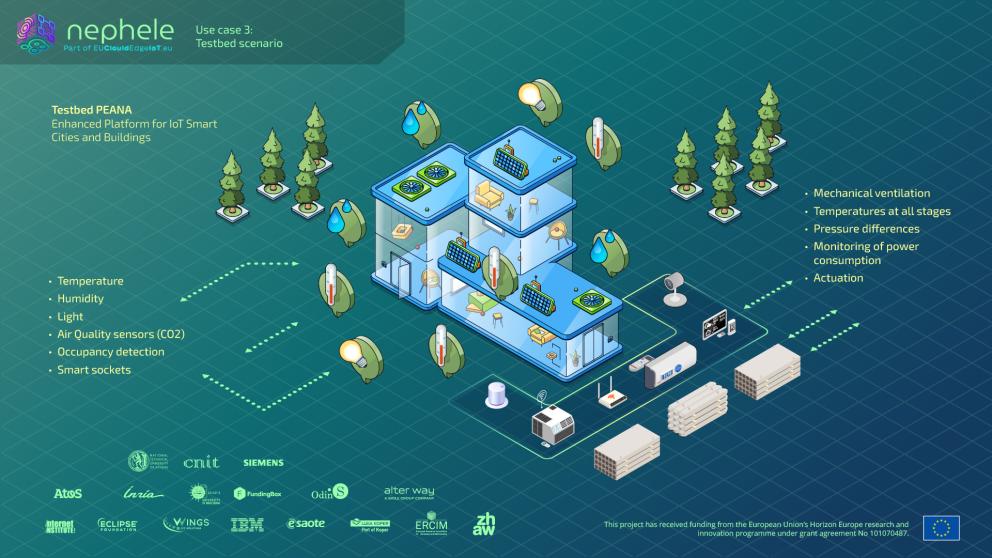
NEPHELE Use Case 3 - Energy Management in Smart Buildings and Cities addresses energy efficiency in our rapidly urbanizing world.
By 2050, we'll have 9.7 billion people on our planet, and 90% of our time will be spent in buildings. The challenge is clear: buildings consume 40% of global energy, with HVAC systems accounting for 50% of that consumption. More concerning is the fact that 30% of HVAC energy is wasted in unoccupied zones due to traditional schedule-based controls, without considering actual room occupancy or usage patterns.
This is where NEPHELE Use Case 3 comes in. Our objective is to create an intelligent, interoperable, and customizable IoT edge-cloud continuum for building energy optimization. This involves improving HVAC energy use based on real-time occupancy data.
Our solution operates on three integrated layers:
- The IoT layer samples environmental sensors and uses mic and tiny ML to detect occupancy in real-time on constrained IoT devices. These devices are intelligent and equipped with adaptable algorithms that adjust their behavior according to the specific environmental conditions of each room.
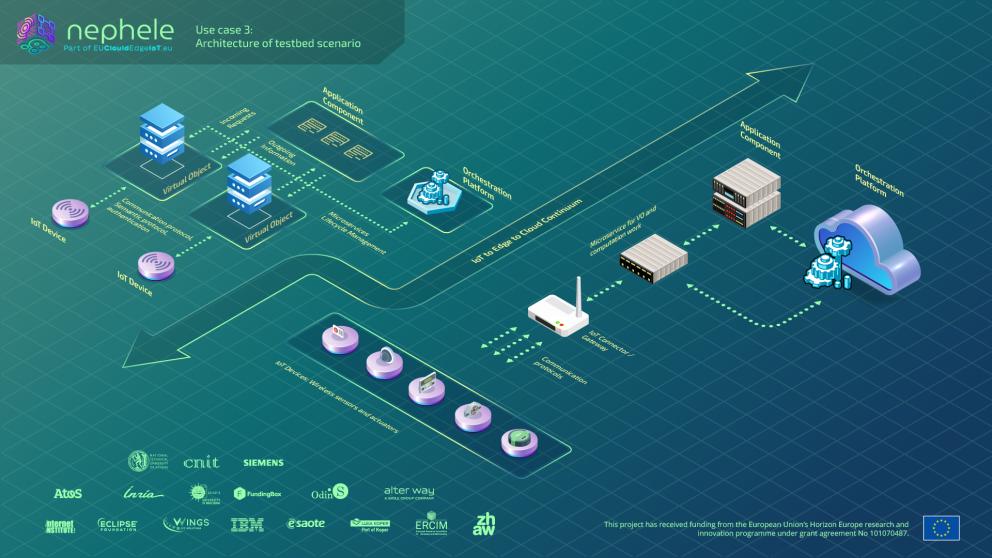
- The Edge layer represents heterogeneous assets as W3C Web of Things virtual objects, providing unified access and interoperability across diverse building systems.
- Our Cloud layer orchestrates composite virtual objects for smart HVAC energy balancing and scheduling using aggregated IoT and edge data.
Moreover, NEPHELE uses synergetic meta-orchestration to support the deployment and life cycle management of distributed applications over programmable multi-cluster computing and networking infrastructure. New sensors and devices to update the system can be easily integrated in short time.
The results speak for themselves:
- Over 21% HVAC energy reduction
- 100% security and trust
- Over 83% user comfort
- 100% system reliability
We run a live demo at Odin's facilities showcasing real-time monitoring, prediction, and intelligent HVAC control. Our research results, such as the Tiny ML engine and MicroEP engine, have been integrated into the Siemens Portfolio Platform 5, which is an end-to-end development suite for resource-limited devices in building automation. Beyond the immediate impact, we have contributed to W3C Web of Things standards.
Study case
Development and evaluation of NEPHELE technologies for intelligent monitoring and remote energy management in a Smart Building testbed scenario provided by OdinS in Murcia, Spain.
Demonstration
- Develop advanced applications and services using the VOStack. This will help to effectively manage building equipment control, prioritizing customized services for energy efficiency, user well-being, and comfort.
- Deploy a sophisticated automation scheme. This allows to collect real-time data from diverse range of IoT devices. These devices include appliances, sensors, and HVAC - heating, ventilation, and air conditioning - systems, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the building's operational status.
- Utilize Edge nodes to instantiate Virtual Objects. These nodes play a vital role in the instantiation of VOs, further enhancing the system’s capacity to process and respond to data in real-time.
- Distribute intelligence across Edge nodes. This will allow the system to operate more efficiently and responsively, avoiding bottlenecks.
Scenarios
Goal
- To develop applications to allow energy control actions of building equipment.
- To offer customized services to end-users to improve energy-efficient and well-being.
- To provide an automation scheme based on real-time information and video/image processing from different IoT devices and Edge nodes.
Description

- Distributed complex decision making for energy efficiency.
- Distributed authorization operations to control HVAC and building equipment
- Video presence detection in building
- Communication radio offloading among Wifi, and Ethernet networks.
- Customizable IoT devices to support energy-efficiency and well-being in buildings
Technical constraints
- Software component orchestration
- Device customization and management
- Device interoperability
- Control Access Management
- Identity Management
- Data storage
- Low latency communication
- Computer vision for information extraction
- Intelligent data filtering/aggregation/compression